Setting up a National Quality Infrastructure
A national quality infrastructure (NQI) is also referred to as a Standards and Conformance Infrastructure. This is the institutional framework that establishes and implements standardisation, including conformity assessment services, metrology, and accreditation.
How to set up a National Quality Infrastructure
As a first step in setting up a quality infrastructure, a government needs to establish three types of central bodies to develop and implement its QI activities:
- a National Metrology Institute (NMI)
- a Legal Metrology Authority (LMA)
- a National Standards Body (NSB)
- a National Accreditation Body (NAB)
The work of these bodies is interrelated.
For a specific example of setting up a quality infrastructure please see, the PTB Publication “The Answer to the Global Quality Challenge: A National Quality Infrastructure”.
National Quality Infrastructure (NQI)
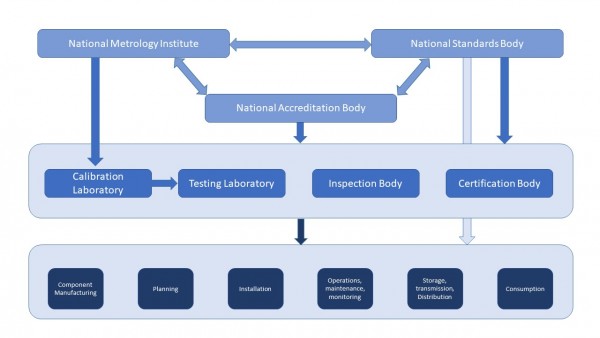
The National Metrology Institute
A national metrology institute (NMI)’s roles and responsibilities include to:
- establish the economy’s national measurement system and ensure its international recognition and acceptance; establish, maintain, develop, promote and disseminate the economy’s peak measurement capabilities traceable to the International System of Units (SI);
- conduct research to improve national references;
- provide advice, support and training to government, industry, commerce and the public on metrology issues;
- develop a sound metrological basis for the national accreditation scheme.
- support the national Legal Metrology Authority in terms of requirements for new legal metrology regulations, calibration and test equipment needed for legal metrology regulations and setting up this equipment; and
- build metrological expertise in the economy.
The NMI is commonly set up within an existing government department and should work closely with the other elements of the NQI.
An economy may identify expert institutes outside the NMI to be responsible for specific peak measurement standards and capabilities. These are “designated institutes” or “DIs”, connected to the NMI as part of the national measurement system.
The NMI and any DIs are part of the international scientific community under the metre convention.
If you want to know more about the role of the international scientific metrology system and associated activities, please see the BIPM website.
Legal Metrology Authority
The national Legal Metrology Authority institute (LMA) may be a separate body or combined with the NMI. Its primary function is to ensure measurements made for regulatory purposes are fit for purpose.
Originally, LMAs were concerned with technical specifications and control of measuring instruments used for trade. Currently they may also be responsible for controls over a broader range of regulatory measurements (including traffic, health and environmental measurements) and for ensuring that appropriate legislation is in place for legal traceability of measurements to facilitate the conversion of measurement data into evidence acceptable in a court of law.
Accordingly, in close cooperation with the NMI, the LMA contributes to metrology policy development and the maintenance and modernization of metrology legislation.
Information on the role and function of an LMA can be found at OIML D 1:2012 Considerations for a law on metrology.
Standards bodies
A national standards body develops standards that:
- promote global trade and innovations
- assure efficiency and quality, and
- help protect the environment and society as a whole.
The standards body works with metrology organisations, regulatory authorities, and government, trade, industry and consumer organisations to promote, develop and/or adopt international standards.
Some standards are voluntary, while others are mandatory and need to be enforced by governmental authorities.
For more information about standards bodies you can visit the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) website and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) website.
Accreditation bodies
A national accreditation body "attests to the competence and impartiality of conformity assessment bodies (testing and calibration laboratories, certification and inspection bodies), according to international standards such as ISO/IEC" (see here).
Why is conformity assessment important?
The conformity assessment work is carried out by calibration laboratories, testing laboratories, inspection bodies and certification bodies.
The process of conformity assessment delivers many benefits to consumers, businesses and governments, including:
- Consumers gain confidence trust in products and services they use.
- Businesses get a competitive edge and can participate in international trade.
- Governments can meet the health, safety and environmental needs of their citizens.
The quality infrastructure must have four types of organisations operating to conduct conformity assessment work - certification bodies, testing laboratories, inspection bodies and calibration laboratories.
NQI Supporting Public Sector Assurance
An effective QI provides Government Agencies and Public Sector Organisations a wide range of tools and systems to demonstrate compliance and support the achievement of policy objectives in a wide range of areas. The Public Sector Assurance website, developed by the global quality infrastructure partners (INetQI) represented by the BIPM, IAF, IEC, ILAC, ISO, ITC, ITU, OIML, UNECE, World Bank Group, WTO and UNIDO provides many useful examples and case studies: https://publicsectorassurance.org/
QI Toolkit
The QI Diagnostics and Reform Toolkit was jointly developed by the World Bank Group and the national metrology institute of Germany, Physikalisch Technische-Bundesanstalt (PTB). It is aimed to help development partners and governments analyse QI ecosystems, provide recommendations to bridge gaps in the ecosystem, support reforms, and build the capacity of institutions. The toolkit is a holistic reference to QI diagnostic tools, reform interventions and approaches, and monitoring and evaluation, and is supported by practical case studies and examples. This toolkit is a great place to start when reforming or developing an NQI: https://www.worldbank.org/en/topic/competitiveness/brief/qi
Another useful reference document:
Ensuring Quality to Gain Access to Global Markets: A Reform Toolkit (full report) (PDF)

